Agro-Ecology: Definitions and Principles
February 15, 2023 2023-03-03 7:29Agro-Ecology: Definitions and Principles
Multiple definitions of AgroEcology
Agroecology as a science is defined as:
(I) the integrated study of the ecology of the complete food system, including ecological, economic, and social components, or, in other words, the ecology of the food system;
(ii) applying ecological concepts and principles to the design and administration of sustainable food systems; and
(iii) integrating research, education, action, and change to bring sustainability to all aspects of the food system: ecological, economic, and social.
Agroecological practices aim to improve agroecosystems by harnessing natural processes, fostering beneficial biological interactions and synergies among their components, and utilizing ecological processes and ecosystem services to the greatest extent possible in the development and implementation of practices.
As a social movement, agroecology is seen as a solution to current challenges such as climate change and malnutrition, in contrast to the so-called “industrial” model, which is being transformed to build locally relevant food systems that strengthen the economic viability of rural areas through short marketing chains and fair and safe food production. It promotes smallholder food production and family farming, farmers and rural communities, food sovereignty, local knowledge, social justice, local identity and culture, and indigenous seed and breed rights. This aspect of agroecology as a political movement is becoming more visible.
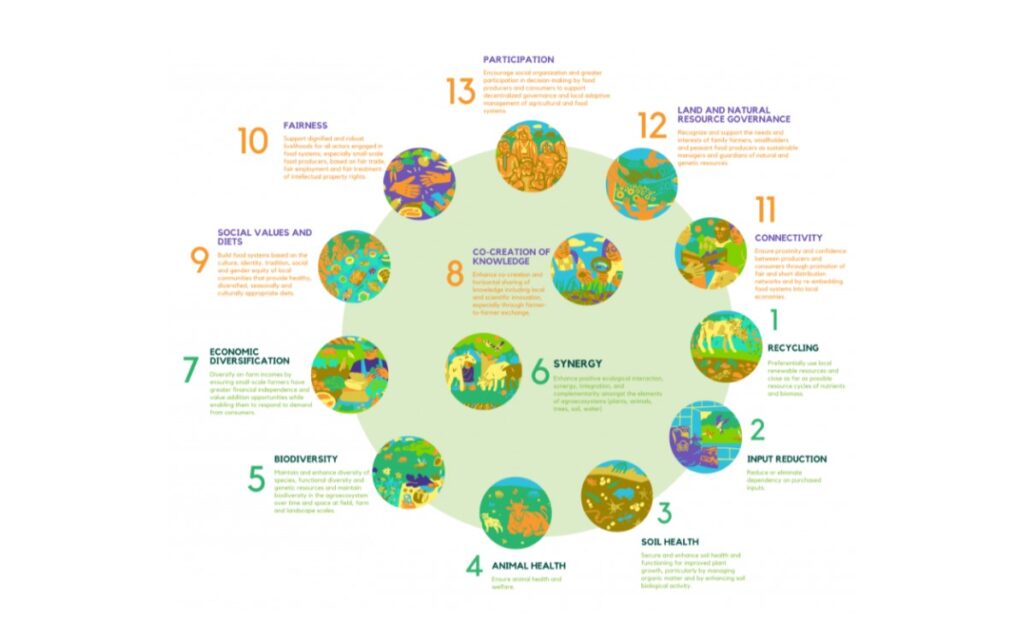
The 13 agroecological principles
Increase resource efficiency.
1. Recycling: Use local renewable resources wherever feasible and keep nutrient and biomass resource cycles as far as possible.
2. Reduce or eliminate reliance on bought inputs to promote self-sufficiency.
Increase your resilience.
3. Soil health: Protect and promote soil health and functioning for better plant development, notably by controlling organic matter and increasing soil biological activity.
4. Animal health: Ensure the health and wellbeing of animals.
5. Biodiversity: Maintain and improve species variety, functional diversity, and genetic resources, and hence total agroecosystem biodiversity in time and space at the field, farm, and landscape scales.
6. Synergy: Improve beneficial ecological interaction, synergy, integration, and complementarity among agroecosystem components (animals, crops, trees, soil and water).
7. Economic diversification: Diversify on-farm revenues by providing small-scale farmers with greater financial freedom and value-added options, allowing them to adapt to consumer demand.
Ensure social equity and accountability
8.Knowledge co-creation: Promote knowledge co-creation and horizontal sharing, including local and scientific innovation, particularly through farmer-to-farmer exchange.
9. Social values and diets: Create food systems based on local communities’ culture, identity, tradition, social and gender equity, and that provide nutritious, diverse, seasonally and culturally appropriate diets.
10. Fairness: Promote dignified and sustainable lifestyles for all food system players, particularly small-scale food producers, through fair trade, fair employment, and fair handling of intellectual property rights.
11. Connectivity: Promote closeness and trust between farmers and customers by encouraging fair and short distribution networks and re-integrating food systems into local economies.
12. Land and natural resource governance: Improve institutional arrangements, including recognition and support for family farmers, smallholders, and peasant food producers as long-term stewards of natural and genetic resources.
13. Participation: Encourage food producers and consumers to organize socially and participate more in decision-making in order to support decentralized governance and local adaptive management of agricultural and food systems.
Sources:
FAO, Agroecology Knowledge Hub. Agroecology definitions (2017)
Agroecology Europe, Our understanding of agroecology (2017)
FAO, The 10 elements of agroecology: guiding the transition to sustainable food and agricultural systems (2018)
Search


